Dengue Fever
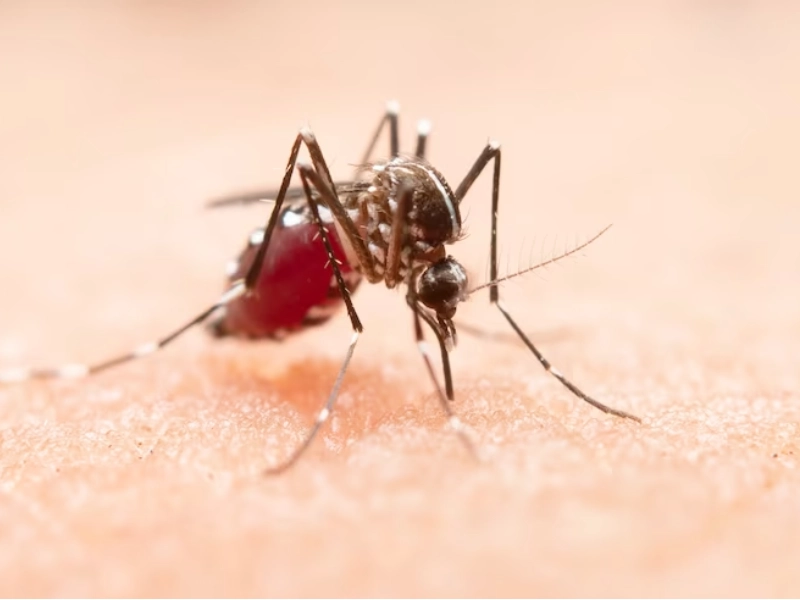
Dengue is a viral disease that is transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. The disease is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, with over half of the world’s population at risk of infection. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 390 million people are infected with dengue every year, with 96 million people exhibiting symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of Dengue
Dengue can manifest in several ways, from mild flu-like symptoms to a more severe and life-threatening form of the disease. The most common symptoms of dengue include:
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Pain behind the eyes
- Joint and muscle pain
- Rash
- Nausea and vomiting
- Mild bleeding, such as nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or easy bruising.
These symptoms typically appear within 4-7 days after a person has been bitten by an infected mosquito. The illness can last for up to 10 days, and in some cases, it can progress to a more severe form of dengue known as severe dengue or dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Transmission of Dengue
Dengue is transmitted through the bite of an Aedes mosquito, which is infected with the dengue virus. The mosquito becomes infected with the virus when it bites a person who has the disease. The virus then multiplies within the mosquito, and when the mosquito bites another person, it passes the virus on to them.
Prevention of Dengue
There is currently no specific treatment for dengue, but early detection and treatment of symptoms can help to reduce the severity of the disease. To prevent dengue, it is essential to control the mosquito population in areas where the disease is prevalent. This can be achieved through the following measures:
Eliminating mosquito breeding sites: This includes removing standing water from areas around the home, such as flowerpots, buckets, and old tires, where mosquitoes can lay their eggs.
Using insect repellents: Applying insect repellents containing DEET or other approved ingredients can help to keep mosquitoes away.
Wearing protective clothing: Wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants can help to reduce the amount of exposed skin, making it more difficult for mosquitoes to bite.
Screening windows and doors: Installing screens on windows and doors can help to keep mosquitoes out of the home.
Using mosquito nets: Sleeping under mosquito nets can help to prevent mosquito bites, particularly in areas where mosquito populations are high.
Conclusion Dengue is a serious public health concern in many parts of the world. Although there is no specific treatment for the disease, early detection and treatment of symptoms can help to reduce the severity of the illness. Preventative measures, such as eliminating mosquito breeding sites, using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and using mosquito nets, can help to reduce the risk of infection. With continued efforts to control mosquito populations and improve access to healthcare, it is possible to reduce the impact of dengue on communities around the world.